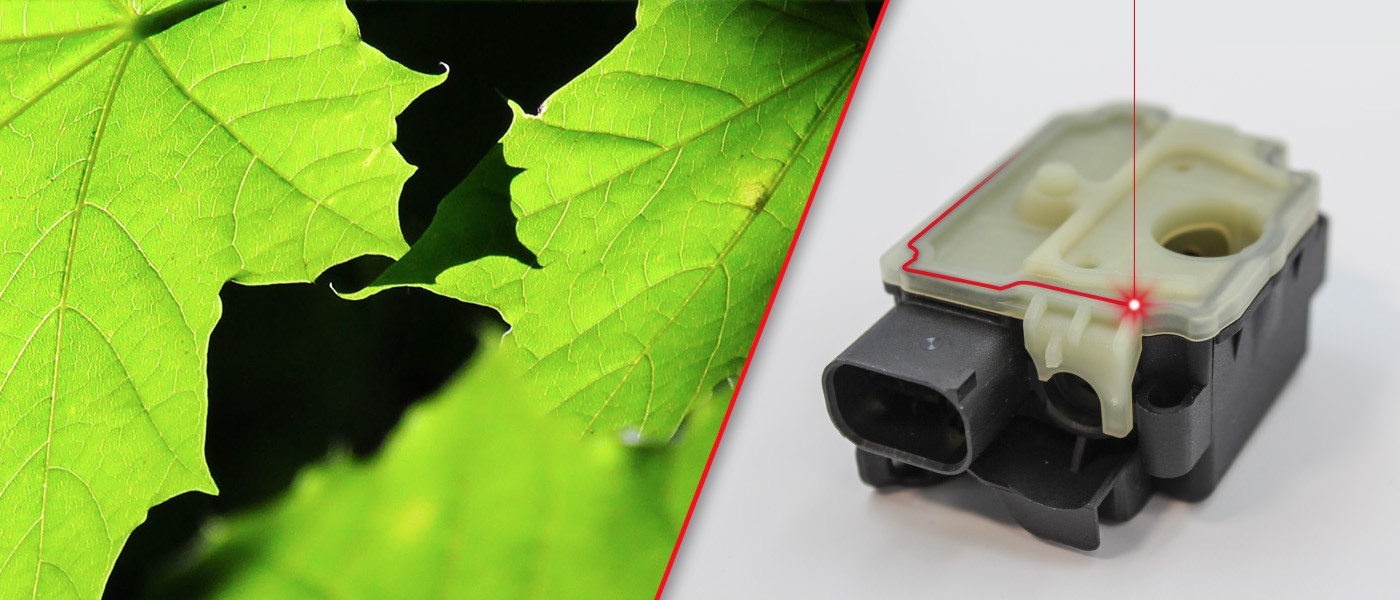
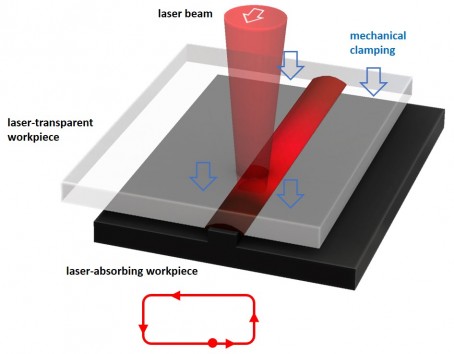
Quasi-simultaneous - melt off as process control
Instead of a single traverse of the welding contour, it is scanned several times per second. The weld seam heats up gradually over its entire length and melts everywhere at the same time. The liquefied plastic is pressed out of the weld seam by clamping pressure and the next layer of plastic continues to melt underneath. Over time, a welding rib in the weld seam melts and a setting path becomes measurable - similar to ultrasonic or vibration welding.
Since the laser beam must be moved very quickly for quasi-simultaneous welding, a galvo scanner is usually used as the optical system. Depending on the lens of the galvo scanner, working fields of different sizes can be scanned. With the size of the working field, however, the size of the spot of the laser beam and the working distance also increase.
The welding rib has a rectangular design and is located in the lower part. This distinguishes laser welding from ultrasonic or vibration welding, where triangular welding ribs are used, which are usually located in the upper part.
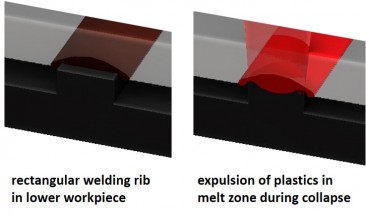
An empty volume can be provided in the design for the escaping melt during collapse in order to catch it selectively. The melt is then not visible from the outside and cannot damage sensitive parts such as electronics inside the parts.
Depending on the material used, one may observes first a extension due to thermal expansion, before the plastic melts and the collapse movement starts. After switching off the laser, the collapse does not stop immediately, as the plastic must first cool down before it finally solidifies and the collapse path ends.
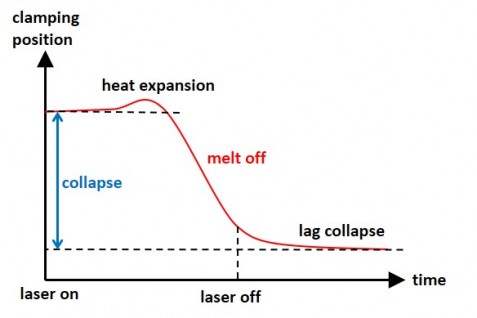
The collapse path can be measured with displacement sensors on the clamping device. The recorded data can be used for process control or quality evaluation.
For quality check the collapse path can be compared with a reference value at a constant welding time.
For active process control, the laser switches off automatically after reaching a preset collapse.
Optics quasi-simultaneous
Process control
Other process types
